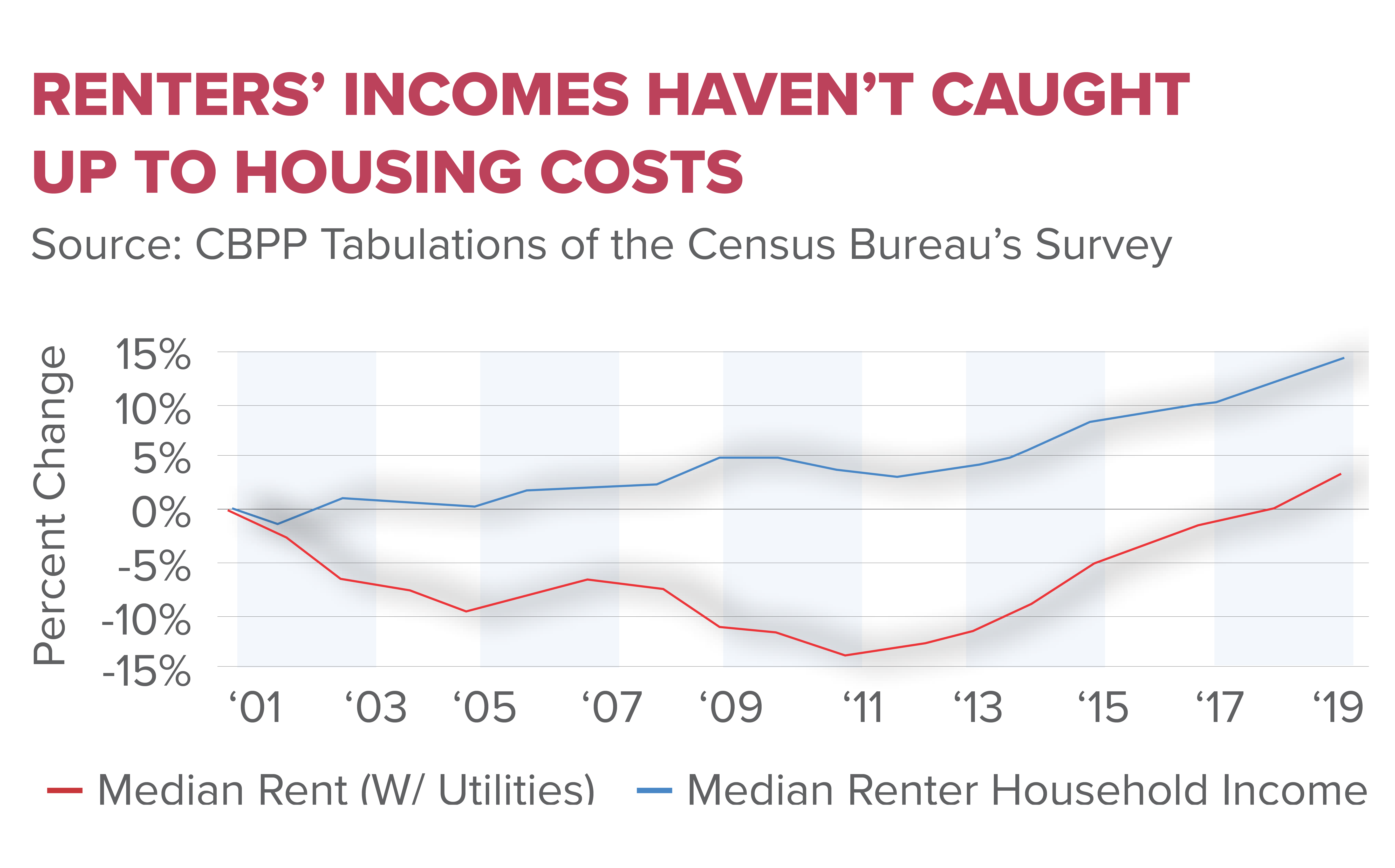
The United States is currently grappling with a housing affordability crisis, an issue more pressing than ever as the cost of new homes continues to skyrocket. Since 1960, the price of a single-family home has more than doubled, leaving many Americans struggling to find affordable options. This crisis is exacerbated by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies and stringent land-use regulations that stifle construction productivity, limiting the ability of builders to respond to the demands of the housing market. As policymakers push for real estate innovation to address these challenges, the growing disparity between housing prices and wages raises urgent questions about future affordability. Addressing the underlying factors contributing to this crisis is crucial for ensuring that all Americans have access to safe and affordable housing options.
The ongoing issue of housing unaffordability poses a significant challenge for countless individuals and families across the nation. With property prices inflating rapidly, many are finding themselves priced out of the market, while various local governments impose restrictive land-use policies that hinder development. The situation calls for a reevaluation of construction practices and the exploration of innovative solutions to enhance housing availability and affordability. As communities wrestle with the consequences of NIMBYism and outdated regulations, there is an urgent need for collaborative efforts to increase housing supply and create pathways toward sustainable living conditions. Only through such thoughtful strategies can we hope to remedy the housing crisis affecting so many lives today.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis in the United States has reached alarming levels, as homeownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many American families. Various factors contribute to this issue, including rising labor and material costs, which have doubled the price of new single-family homes since 1960. However, this crisis is not solely a result of economic fluctuations; it is exacerbated by restrictive housing policies that limit development and innovation within the construction industry. As builders face heightened land-use regulations and community opposition, the ability to meet the growing demand for affordable housing becomes severely diminished.
In essence, the housing affordability crisis underscores the interplay between market dynamics and government policies. While economic growth has propelled other sectors forward, the construction industry has lagged behind due to increasingly stringent regulations. Regions plagued by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) sentiment hinder large-scale housing projects that could alleviate the housing shortage. As communities prioritize their immediate interests over broader housing needs, the challenge of finding affordable homes becomes ever more acute, calling for a reevaluation of land-use regulations that stifle growth.
The Impact of NIMBY Policies on Housing Development
NIMBY policies significantly hinder the development of new housing projects, contributing to the broader housing affordability crisis. These regulations often arise from residents’ desires to maintain the character of their neighborhoods, leading to opposition against larger construction projects. Such resistance can result in smaller, more costly developments that fail to address the growing demand for affordable housing. As builders struggle to navigate a labyrinth of planning approvals, community input, and restrictive zoning laws, the overall productivity of the construction sector diminishes, aggravating the housing crisis.
Furthermore, the adverse effects of NIMBY policies extend beyond immediate project delays. The construction market becomes fragmented as smaller firms that adhere to these regulations emerge, leading to a decline in innovation and efficiency. Research indicates that larger builders, capable of leveraging economies of scale, produce housing more effectively than smaller competitors often constrained by local regulations. As a result, the lack of large-scale projects fosters a stagnation in housing supply, exacerbating costs and limiting options for potential homeowners.
Boosting Construction Productivity amid Land-Use Regulations
Enhancing construction productivity is crucial in addressing the housing affordability crisis, particularly in light of restrictive land-use regulations. The historical data shows that productivity in the construction sector has significantly lagged behind other industries, especially since 1970 when regulation increased. Builders face mounting challenges related to expanding their operations within increasingly narrow boundaries set by local governments and community preferences, which leads to a decrease in large residential projects. Therefore, incentivizing innovation and efficiency in construction processes is vital to counteracting these regulatory challenges.
Strategies to improve productivity include adopting advanced construction technologies and methodologies that allow for greater flexibility and responsiveness to regulations. Emphasizing real estate innovation, such as modular and prefabricated housing solutions, can also foster a more adaptable building environment. By streamlining the construction process and minimizing regulatory overhead, builders can produce homes at lower costs, thus making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
Land-Use Regulations and Their Hidden Costs
Land-use regulations often come with hidden costs that significantly elevate housing prices. While these regulations are designed to protect community interests, they often inadvertently restrict housing supply, making it difficult for developers to respond to market demand. The result is a decrease in available housing options, driving prices higher and contributing to the growing crisis of affordability. The research highlights that as regulations become more complex, builders are less likely to undertake new projects, which compounds the existing housing shortage.
Moreover, the costs associated with compliance—such as lengthy approvals, design alterations, and community consultations—further inhibit the construction of affordable homes. Builders operating under stringent regulations are forced to pass these expenses onto consumers, ultimately contributing to inflated housing costs. Consequently, a reevaluation of land-use policies is essential in order to facilitate a more robust and productive housing market that can meet the needs of a diverse population.
Real Estate Innovation as a Key to Solving the Crisis
Real estate innovation has the potential to revolutionize the housing market, particularly when it comes to affordability. By embracing new technologies and methods, such as 3D printing, smart home designs, and sustainable building practices, the industry can create homes that are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly. These advancements can streamline construction processes, lower production costs, and ultimately provide more affordable housing options for consumers. Real estate innovation is essential for addressing the pressing challenges posed by restrictive regulations and rising demand.
Incorporating innovative materials and efficient building techniques can significantly enhance construction productivity while minimizing waste. Additionally, leveraging data analytics and AI-driven solutions can optimize project planning and execution, further enhancing the efficiency of the construction sector. By fostering a culture of innovation within real estate, stakeholders can effectively combat the housing affordability crisis and create sustainable living environments that meet the needs of contemporary society.
The Role of Government in Housing Market Regulation
Government plays a pivotal role in shaping the housing market through regulations and policies. While intended to safeguard community interests, policies such as zoning laws and building codes can often lead to unintended consequences, stifling development and innovation within the industry. Striking a balance between necessary regulation and the promotion of housing growth is crucial for addressing the affordability crisis. Policymakers must consider the long-term implications of restrictive regulations on housing availability and affordability.
Engaging stakeholders in the conversation around housing regulations is vital for creating effective policies. Encouraging community input while educating residents on the broader implications of NIMBYism can foster a more progressive approach to development. Moreover, revising outdated land-use regulations to allow for larger and more efficient housing projects can facilitate a healthier real estate market. By taking proactive measures, the government can help mitigate the housing affordability crisis and promote a more inclusive housing landscape.
Historical Perspectives on Housing Construction Trends
Understanding the historical context of housing construction trends provides valuable insights into current challenges. From post-WWII America’s construction boom, which saw large-scale developments flourish, to the restrictive environment of today, the evolution of the housing market reflects broader economic and social changes. During the mid-20th century, builders capitalized on large parcels of land and economies of scale to meet housing demand effectively. However, as NIMBY sentiment grew and regulations tightened, the scale of projects significantly diminished.
The decline in productivity has profound implications for housing affordability and access. The present state of the construction sector features smaller firms that may not have the resources for innovation, leading to stagnant growth. Reflecting on past successes can inform future approaches to enhancing productivity and fostering housing construction that meets today’s challenges. A renewed focus on large-scale developments and removing regulatory bottlenecks could revitalize the construction industry and increase the availability of affordable homes.
Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Housing Models
In the quest for affordable housing, exploring alternatives to traditional housing models has become increasingly necessary. Co-housing, tiny homes, and modular housing represent innovative solutions that respond to contemporary economic realities while circumventing some regulatory challenges faced by conventional developers. These alternatives not only maximize land-use efficiency but also promote community engagement and sustainability. By diversifying housing options, cities can better meet the needs of a growing population without overwhelming existing infrastructure or regulations.
Moreover, these alternatives often require less land than typical single-family homes, making them attractive in regions where land-use regulations pose significant barriers to development. These models can facilitate rapid construction and adaptability to market trends while providing affordable options for consumers. Encouraging the adoption of diverse housing typologies can ultimately ease the pressures of the housing affordability crisis and promote more inclusive urban environments that cater to a broader spectrum of residents.
The Future of Housing: Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of housing and inform policy decisions moving forward. The increasing focus on sustainability and resilient design can lead to innovations that make housing more affordable and energy-efficient. Smart technologies in home construction can automate processes, enhance energy use, and enable inhabitants to manage resources more effectively. These shifts mark a pivotal change in how homes are built and perceived, necessitating a reevaluation of existing regulations to accommodate new technologies and practices.
Additionally, fostering collaboration between the public and private sectors can address housing challenges more effectively. By creating policy frameworks that facilitate innovation while also meeting community needs, stakeholders can work towards solutions that address housing shortages without sacrificing quality or environmental standards. As the housing landscape continues to evolve, integrating innovative approaches and responsive regulations will be crucial in resolving the affordability crisis and ensuring that housing remains accessible for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of NIMBY policies on the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY policies, or ‘Not In My Backyard,’ refer to local opposition against new housing developments. These policies significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by hindering the construction of new homes, which decreases supply and drives up prices. This limits access for potential homebuyers and renters, further exacerbating affordability issues.
How do land-use regulations influence the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations often impose strict zoning laws and development controls that restrict the types and densities of housing that can be built. These regulations can stifle construction productivity, leading to fewer housing units being developed. As a result, the limited supply fails to meet demand, contributing to the housing affordability crisis.
What role does construction productivity play in the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity is crucial in determining housing costs. When construction productivity declines, fewer homes are built at a lower cost. This stagnation in productivity, often linked to restrictive land-use policies and smaller project scales, directly contributes to the rising costs of housing, worsening the affordability crisis.
How have real estate innovations been affected by the housing affordability crisis?
Innovations in real estate, such as modular and prefabricated construction methods, can help alleviate the housing affordability crisis by reducing costs and increasing supply. However, strict land-use regulations and NIMBYism have limited the adoption of these innovations in residential building, thereby hindering overall progress in making housing more affordable.
What are the connections between the housing market and the affordability crisis?
The housing market is directly impacted by the affordability crisis through the rising prices of homes due to limited supply and high demand. Factors such as NIMBY policies, land-use regulations, and a lack of construction productivity prevent the adequate development of affordable housing options, further straining the market for prospective buyers and renters.
Why is ownership increasingly out of reach for Americans amid the housing affordability crisis?
Ownership is becoming increasingly unattainable due to skyrocketing home prices, which have more than doubled since 1960. Contributing factors include rising labor and material costs, stringent land-use regulations, and a decline in construction productivity caused by policies that limit large-scale developments, all of which fuel the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
What economic repercussions stem from the housing affordability crisis?
The housing affordability crisis has significant economic repercussions, including intergenerational wealth transfer and declining home equity for younger demographics. As homeownership becomes less accessible, younger Americans struggle to build wealth through real estate, leading to broader economic inequality and hampered economic growth.
How can addressing construction productivity help resolve the housing affordability crisis?
Improving construction productivity can address the housing affordability crisis by enabling builders to produce more homes at lower costs. This requires reducing regulatory burdens and fostering an environment conducive to innovation and large-scale development, thereby increasing the housing supply and making homes more affordable.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | Housing prices have more than doubled since 1960, impacting accessibility for many Americans. |
| NIMBY Policies | ‘Not In My Backyard’ policies have stifled large-scale building projects and contributed to high housing costs. |
| Construction Productivity Decline | The productivity of the construction sector fell by 40% from 1970 to 2000, despite growth in other sectors. |
| Impact of Regulation | Increased land-use regulations have led to smaller construction firms and less innovation. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are losing out on housing wealth compared to older homeowners. |
| Historical Data Analysis | Analysis shows a steep increase in housing productivity from 1935 to 1970, followed by stagnation. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that has evolved due to a combination of factors, primarily influenced by restrictive land-use policies and declining construction productivity. These NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) regulations have hindered the ability to build large-scale and cost-effective housing projects, rendering homeownership unattainable for many Americans. With home prices having more than doubled since 1960, and the decline in housing construction productivity since the 1970s, there is an urgent need for reform to ensure housing remains accessible. Addressing these challenges is essential for fostering economic stability and ensuring that future generations can achieve the dream of homeownership.