Income inequality is an urgent concern that has sparked intense debate worldwide. As the rich grow richer, the wealth distribution becomes increasingly lopsided, raising questions about economic justice and the implications for society. The immense fortunes of billionaires can drive philanthropy and wealth redistribution efforts, yet they also raise ethical dilemmas about how wealth concentration impacts the environment and community well-being. Discussions around this topic often include the effectiveness of billionaire-led initiatives, probing whether their influence serves to uplift the underprivileged or perpetuates their struggles. Ultimately, addressing income inequality requires a nuanced understanding of the balance between wealth creation and equitable resource allocation.
The disparity in financial resources among different segments of society, often referred to as wealth gap or economic inequality, poses significant challenges. Conversations surrounding the influence of affluent individuals and their contributions to societal improvement are becoming increasingly prevalent. The moral implications of their wealth and the potential for addressing systemic issues through the reallocation of resources cannot be ignored. Moreover, the consequences of extreme wealth on the environment and public governance bring forth the concept of economic equity, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to reduce disparities. Exploring these themes helps us understand the complex dynamics of wealth concentration and its effects on broader societal wellness.
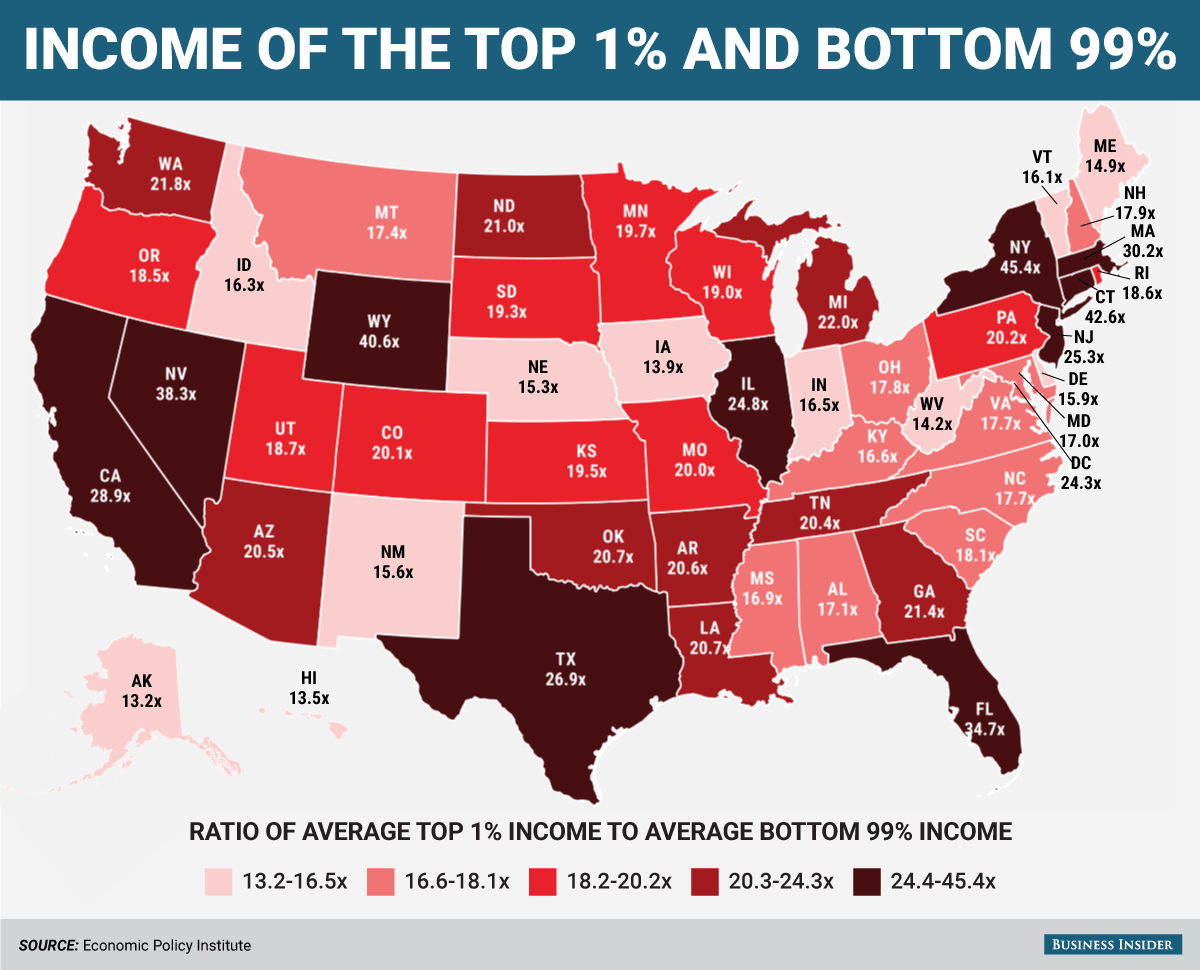
The Impact of Income Inequality on Society
Income inequality has emerged as a pervasive issue that affects the fabric of society, leading to various economic and social tensions. When wealth is concentrated in the hands of a few, the gap between the rich and the poor widens, affecting access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and housing. This disparity fosters feelings of discontent among lower-income groups, who often feel marginalized and excluded from the opportunities that wealth could provide. Moreover, as income inequality grows, it poses risks to social cohesion, as the divide can breed resentment and conflict among different socio-economic classes.
The effects of income inequality extend beyond just economic disadvantages; they can also manifest in the degradation of public trust in institutions and government. When a society witnesses extreme wealth concentrated among a small elite, it raises questions about the fairness of economic systems and the role of public officials, who may be perceived as being ‘in the pocket’ of the wealthy. This perception can undermine democratic principles, leading to calls for reforms aimed at redistributing wealth and ensuring that opportunities are accessible to all, not just a select few.
Billionaires: Benefactors or Detractors?
The debate surrounding the role of billionaires in society often presents them as either benefactors or detractors. On one hand, proponents argue that billionaires, such as Bill Gates and others, have made significant contributions to society through philanthropy, directing vast resources towards initiatives such as global health and climate change. Their ability to mobilize funds and innovate can lead to developments that benefit society at large, addressing pressing issues effectively. This viewpoint highlights the potential of wealthy individuals to act as catalysts for positive change, driving advancements that may not be achievable through traditional governmental means.
Conversely, critics argue that the very existence of billionaires reveals systemic flaws in the economic structure that prioritizes wealth accumulation over equitable distribution. This view posits that excessive wealth can have harmful societal implications, such as political influence that skews priorities away from the common good and undermines democracy. Additionally, as Tom Malleson noted during the discussion, the environmental impact of extreme wealth cannot be ignored, as billionaires often contribute disproportionately to carbon emissions and resource exploitation. Thus, the question remains: do the benefits of billionaire philanthropy outweigh the overall societal costs of such economic imbalance?
Lessons from Wealth Redistribution
Redistribution of wealth has been a contentious point in economic discussions, particularly in addressing income inequality and enhancing social justice. Effective wealth redistribution can serve as a mechanism for improving the living conditions of the poorest segments of society. The debate on whether billionaires should be taxed more heavily to fund public welfare programs highlights the complexities of achieving economic justice through redistribution. Advocates for wealth redistribution suggest that redirecting funds from the super-rich to public services can help provide basic needs, such as healthcare, education, and housing, improving the standards of living for many.
Nevertheless, opponents of heavy taxation argue that it could stifle innovation and economic growth. Critics assert that billionaires contribute to job creation and economic development by investing their wealth. The challenge thus lies in finding a balanced approach that ensures fair wealth distribution while also promoting a healthy economy. Solutions can include progressive taxation, which taxes higher income earners at larger percentages, or introducing mechanisms that encourage philanthropic engagement from billionaires, allowing them a stake in the socio-economic development of their communities.
Philanthropy and Its Ethical Implications
Philanthropy plays a crucial role in the contemporary discussion around wealth and its distribution, acting as both a positive force and a topic of ethical scrutiny. While charitable giving can address immediate needs in sectors like education, healthcare, and disaster relief, it raises questions about the motivations behind such actions. Critics argue that philanthropy often falls short of addressing the root causes of poverty and inequality, while allowing the wealthy to maintain control over how resources are distributed, which can perpetuate systemic inequalities. This dilemma invites a closer examination of the ethical implications of philanthropy amidst extreme wealth.
Additionally, the influence of philanthropic efforts can shape public policy and societal priorities, steering focus toward issues favored by wealthy donors rather than those most pressing for the broader population. Discussions about the ethics of philanthropy often revolve around the notion of ‘effective altruism’—the idea that actions should yield the greatest good for the greatest number. This raises the need for a reevaluation of traditional philanthropic models to ensure they are not merely band-aid solutions but are genuinely contributing to sustainable social change and equality.
Reimagining Economic Justice for All
The pursuit of economic justice is increasingly seen as essential for building a just and equitable society. Economic justice encompasses more than just fair wages and working conditions; it calls for systemic changes that address the underlying factors contributing to income inequality. The broadening of this definition urges society to consider environmental sustainability, labor rights, and corporate responsibility as integral components of economic health. Advocates for economic justice argue that these principles must be at the forefront of policy-making to ensure that wealth is not only created but is distributed in a manner that uplifts the entire population.
Implementing frameworks that facilitate economic justice often requires innovative solutions, such as the incorporation of stakeholder theories in business practices, which recognize the interests of all parties affected by corporate actions. This approach can bridge the gap between profit motives and social responsibility, ensuring that businesses operate in a manner that supports the community at large. For societies grappling with economic disparity, such frameworks present an opportunity for reform that prioritizes both the wellbeing of individuals and the collective health of the economy.
Environmental Concerns and Wealth Concentration
The intersection of environmental issues and wealth concentration has become increasingly prominent in discussions about sustainable economic practices. As highlighted by Tom Malleson, the carbon footprints of the wealthiest individuals can dwarf those of billions of people living at lower socio-economic levels. This reality underscores a critical conversation about the impact of extreme wealth on environmental degradation and climate change. To combat these challenges, advocates argue for the need to redistribute wealth towards green technologies and sustainable development, positing that investing in innovation can lead to both economic growth and environmental sustainability.
Conversely, this discourse also raises questions about the accountability of wealthy individuals and corporations in environmental stewardship. As billionaires amass wealth, their environmental practices should reflect a commitment to reducing ecological harm. By integrating principles of sustainability into business strategies, wealth creators can play a leading role in combating climate change while exemplifying responsible capitalism. This dual focus on wealth creation and environmental responsibility is crucial in ensuring long-term prosperity for both the economy and the planet.
The Role of Market Dynamics in Wealth Generation
Market dynamics profoundly influence wealth generation and distribution, shaping the economic landscape in which both billionaires and average citizens operate. The argument posits that a thriving market economy generates opportunities for wealth creation, potentially benefiting those at all levels of society. Proponents of this view argue that a capitalist system incentivizes innovation, leading to advancements that can uplift the socio-economically disadvantaged by providing jobs and improving living standards. This perception promotes the idea that a free market, while imperfect, can lead to better outcomes for the majority.
However, critics argue that unregulated market dynamics can exacerbate income inequality, benefitting the wealthy at the expense of the working class. The reliance on market mechanisms to address systemic issues often overlooks the necessity for regulatory frameworks that protect vulnerable populations. As such, discussions around market dynamics must include calls for reforms that ensure equitable access to opportunities and challenge the structures that facilitate wealth concentration among the richest individuals. Addressing these concerns is vital for creating a sustainable economy that serves everyone.
Global Perspectives on Wealth and Inequality
Examining wealth and inequality through a global lens reveals distinct patterns and practices that illustrate diverse responses to economic disparities. In countries like Sweden, which has a higher number of billionaires per capita than the United States, the relationship between wealth accumulation and social welfare systems provides a compelling case study. Sweden’s model demonstrates that a robust market economy can coexist with comprehensive social safety nets, suggesting that strategic policies can enhance both wealth generation and equitable distribution.
On the other hand, nations struggling with high levels of income inequality face unique challenges that complicate wealth distribution efforts. Differences in governance, cultural attitudes toward wealth, and economic structures influence how societies address inequalities. For instance, the imbalance seen in many developing nations showcases the detrimental impacts of global capitalism, where wealth extraction can result in significant social upheaval. These global discussions inform strategies that can be tailored to specific contexts, emphasizing the need for adaptable responses to the multifaceted nature of wealth and inequality.
Rethinking Democracy in the Age of Billionaires
The increasing prominence of billionaires in contemporary democracies necessitates a reevaluation of democratic principles and practices. The influence of wealthy individuals on politics raises questions about the integrity of democratic systems and the fairness of political processes. Critics contend that when billionaires wield disproportionate influence over policy-making, the foundational tenets of democracy—equity, representation, and accountability—are jeopardized. This dialogue encourages society to seek solutions that mitigate the political power of wealth and promote a more equitable approach to governance.
One suggested approach involves increasing transparency in political donations and lobbying efforts, as well as exploring mechanisms like public financing of campaigns. Such reforms aim to level the playing field, ensuring that political representation is not skewed in favor of the wealthy elite. Additionally, encouraging civic engagement and fostering a culture of political responsibility can empower citizens to reclaim democracy from the clutches of wealthy interests. Ultimately, rethinking democracy in an age of billionaires calls for a collective commitment to uphold the values of fairness and representation for all citizens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between income inequality and wealth distribution in society?
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution of wealth among individuals or groups in a society. The extent of income inequality impacts wealth distribution, with a small percentage of the population holding a disproportionately large amount of wealth, leading to disparities in access to resources and opportunities. Addressing income inequality often involves redistributing wealth through policies like progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and investment in public services.
How do billionaires affect income inequality in today’s economy?
Billionaires can significantly impact income inequality by accumulating vast wealth that often outpaces the average income growth for the rest of the population. Their financial power allows them to influence political and economic systems, potentially exacerbating income inequality. However, some argue that billionaires also contribute to economic growth and job creation, thus helping to mitigate extreme disparities. The challenge lies in finding a balance between fostering innovation and addressing the widening gap in income distribution.
What role does philanthropy play in addressing income inequality?
Philanthropy can play a significant role in addressing income inequality by funding initiatives that support education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation. Wealthy individuals and organizations often allocate resources to programs aimed at reducing inequalities and providing opportunities for the less fortunate. However, the effectiveness of philanthropy in bringing about systemic change is debated, with some arguing that it should not replace government responsibility for addressing income inequality through policies and taxation.
Can redistribution of wealth effectively reduce income inequality?
Redistribution of wealth can be an effective strategy for reducing income inequality. Policies such as progressive taxation and social welfare systems aim to redistribute wealth from higher-income individuals to those with lower incomes, thus promoting a more equitable society. By providing essential services and support to disadvantaged groups, redistribution efforts can help level the playing field and enhance economic justice, ultimately leading to a decrease in income disparities.
What is the connection between economic justice and income inequality?
Economic justice is fundamentally linked to income inequality, as it advocates for fair distribution of resources and opportunities within society. When income inequality is high, economic justice is compromised, leading to social unrest and dissatisfaction. Achieving economic justice often requires addressing the root causes of income inequality through policies that promote equitable access to education, employment, and healthcare, ensuring that all individuals have the means to thrive.
How does the concentration of wealth among billionaires impact economic systems?
The concentration of wealth among billionaires can create significant distortions in economic systems. It can lead to unequal access to political influence, perpetuating policies that favor the wealthy and exacerbate income inequality. Additionally, this concentration may stifle competition and innovation as wealthy individuals or corporations monopolize markets. To mitigate these effects, advocates argue for increased regulation, taxation, and policies aimed at enhancing corporate responsibility and economic equity.
| Key Point | Discussion |
|---|---|
| Billionaires and Philanthropy | Debate about whether extreme wealth is beneficial or harmful. Proponents argue billionaires invest in anti-poverty and green initiatives. |
| The Environmental Impact | Critics highlight that the wealthiest emit significant carbon, potentially exacerbating climate issues. |
| Inequality and Democracy | Discussion on whether a system can exist where trillionaires are justified while ensuring basic needs. |
| Walmart’s Role | The company’s practices are critiqued for worker exploitation but are defended for low prices benefiting low-income families. |
| Possible Solutions | Participants propose alternatives like democratic socialism, supportive of labor rights and community wealth distribution. |
| Property-Owning Democracy | A concept proposed for maintaining market exchange while ensuring a more equal property distribution. |
| Immigration as a Solution | Argued as a means to improve life for the world’s poor by providing them with opportunities in wealthier nations. |
Summary
Income inequality remains a pressing issue in today’s society, sparking debates among economists, policymakers, and social theorists. The ongoing discussions reveal a complex landscape where extreme wealth can generate both positive and negative repercussions. Efforts to address income inequality must balance the benefits of wealth creation with the need for equitable distribution and environmental sustainability.